ACOUSTIC INTERFACE

Guitar is the name of a musical instrument recognized by everyone and everywhere. The name itself (and the concept of the instrument) is derived from the greek word Khitara. In ancient Greece, 2500 years ago, the Khitara was just a Lyre with a resonant cavity in order to amplify the sonic power of the Lyre. In Digitl, the Acoustic Interface remains connected with this conceptual approach.
The Lyre, the precursor of Guitar, is just a group of Strings with a particular tension that defines a tuning, a chord. The word Chord (a group of different Tones) itself means String. Music and Harmony are intrinsically connected with these words.
String is a 1-dimensional resonant object, the most simple mathematical object in a dynamic reality. It's defined by a point oscillation in one dimension and the amplitude of the oscillation defines the Length of the String. Resonance (Re-Creation of Sound) is the Process happening in Time that is the inception of Sound. The String has an intrinsic resonant Frequency linked with the Length. In 1-dimensional Space the Modes of Vibration (Frequencies) are relatively simple and basic. This is related with the family of musical instruments named Chordophones, literally meaning "... that use Strings in order to generate sound".
An extension with an extra dimension creates a 2-D surface, that defines the second type of resonant object, configures different structures in 2-D Space with more complex Modes of Vibration (Sound). This defines the family of instruments known as Membranophones, or Percussion. These are any kind of Drums hitted, but we can include in the 2-D surface family of instruments also some part of the Idiophone (Mallets, Marimbas, Xylophone....etc) or the primordial Litophones, that the Fundamental Resonant Frequency of the object is defined mainly by the 2-D surface.
Following this scheme, the 3-D volumetric resonant object defines the family of instruments known as Aerophones, or Wind instruments, because the Resonant Vibration of the Air in a Cavity with higher degrees of complexity in the Modes of Vibration, is the genesis of the Sound. The Flute is the primordial instrument of this type. Bells is an Idiophone clearly defined by a 3-D Resonant Volume, but here is considered more like a 2-D Surface. This is not an absolut definition.
Of course, Space in Reality is and only it can be, a 3-D phenomenon. Sound is necessarily a 3-D phenomenon, a Resonant Vibration, and it's considered by ancient Cosmovisions like the Beginning of Reality itself. And that is the link with the importance of the Guitar (Khitara) on this writing. The Resonant Box that we can see perfectly defined in the following pictures, the primordial Amplification, is the definition of the concept of "Guitar": a 3-D Resonant Object, but with the Fundamental Strings providing the main character. These pictures are from Roman culture derived from precursor Greece.



The main object of these instruments is the String that generates a fundamental Frequency. At that time, the study of the properties of the vibrating String, and the harmonics, was a very important matter in Phylosophy and Mathematics, exemplified by Pythagoras and the study of proportions. For that, it was used the device known as Monochord, a String used to study the harmonic relations, that consequently led to the establishment of the Harmony based on the consonance (pleasant) of the first few harmonics , or arithmetic proportions. "Arithmos" means Number in Greek, and then we have basic perfect numerical proportions: 2/1, 3/2, 4/3, 5/4 , the first approach to Musical Harmony.
The following figures shows the String of the Monochord (literally "One String"). The image of the center shows a vision of Robert Fludd in 1618 of a Celestial/Divine Monochord linking the Ptolemaic Universe with Musical Intervals.



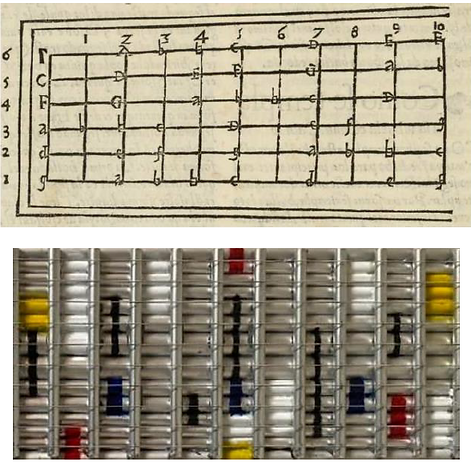
But the definition of the actual Guitar can be traced back to XIII century in Spain, the name "Guitarra" was used to differentiate the instrument from other "Lute" more common in other parts of Europe. All these instruments are "Fretted" instruments, that means the presence of Frets that defines the proportion of the String for every position.



The following image shows the Amat's treatise published in Barcelona in 1586, with the word "Guitarra" clearly depicted. The evolution of this "popular" instrument led to the creation of the actual definition of guitar type Torres, a spanish Luthier . In the image, Francisco Tárrega with one Torres Guitar that establish the main aspect of the actual "Classical" guitar.


The following image shows the XXth century situation, with the "new" Electric Guitar like the paradigm of Popular Music. Guitar is an instrument with an imperfect 12 -Tone Equal Temperament, or 12-TET, created with a particular positioning of Frets, that is: Logarithmic.


Logarithm is Logos (Ratio) and Arithmos (Number), that is again the pythagorical concept of proportions (ratios) of numbers (frequencies).
Ratio (that means also Reason...) is a multiplication or division by a factor. In this case we have the one factor closed to 1.06 ( or in percentage: 6%) that is the Musical SemiTonein a 12-TET system. That means that if we multiply any given Frequency by 1.06 (or increase of 6%), the new frequency would be 1 Semitone higher, also known like a Passing Tone. If we multiply again by 1.06, the new Frequency would be one Musical Tone higher than the original, that is the Melodic Tone. Our Ears are naturally designed to interpret these basic Ratios in an effective way.


Until here the introductory text to contextualize the main feature of the instrument DIGITL, an instrument that requires the use of Digital Processing and Signal Analysis based on Computer systems. For that reason, the logarithmic separation between Frets of the Guitar, is transcended to a linear separation, and every Fret is separated 2 cm from the adjacent ones. It's a digital equivalence with the mechanical advent of the Keyboard in order to linearize the control of the movement of the hands in instruments like Organ, Harpsichord, Pianoforte, etc...